API Reference Guide
The Causely API enables developers to integrate root cause analysis capabilities into their applications and workflows. This comprehensive guide provides step-by-step examples for authentication, querying defects, and automating incident response using the Causely platform.
Getting Started with Causely API
Create API Client Credentials
Before you can use the Causely API, you need to generate API client credentials (Client ID and Secret) from the Causely platform:
-
Login to Causely:
- Go to Causely Portal
- Login with your credentials
-
Navigate to Personal Tokens:
- Click on the Profile Icon in the top-right corner
- Select "Admin Portal"
- Choose "Personal Tokens"
-
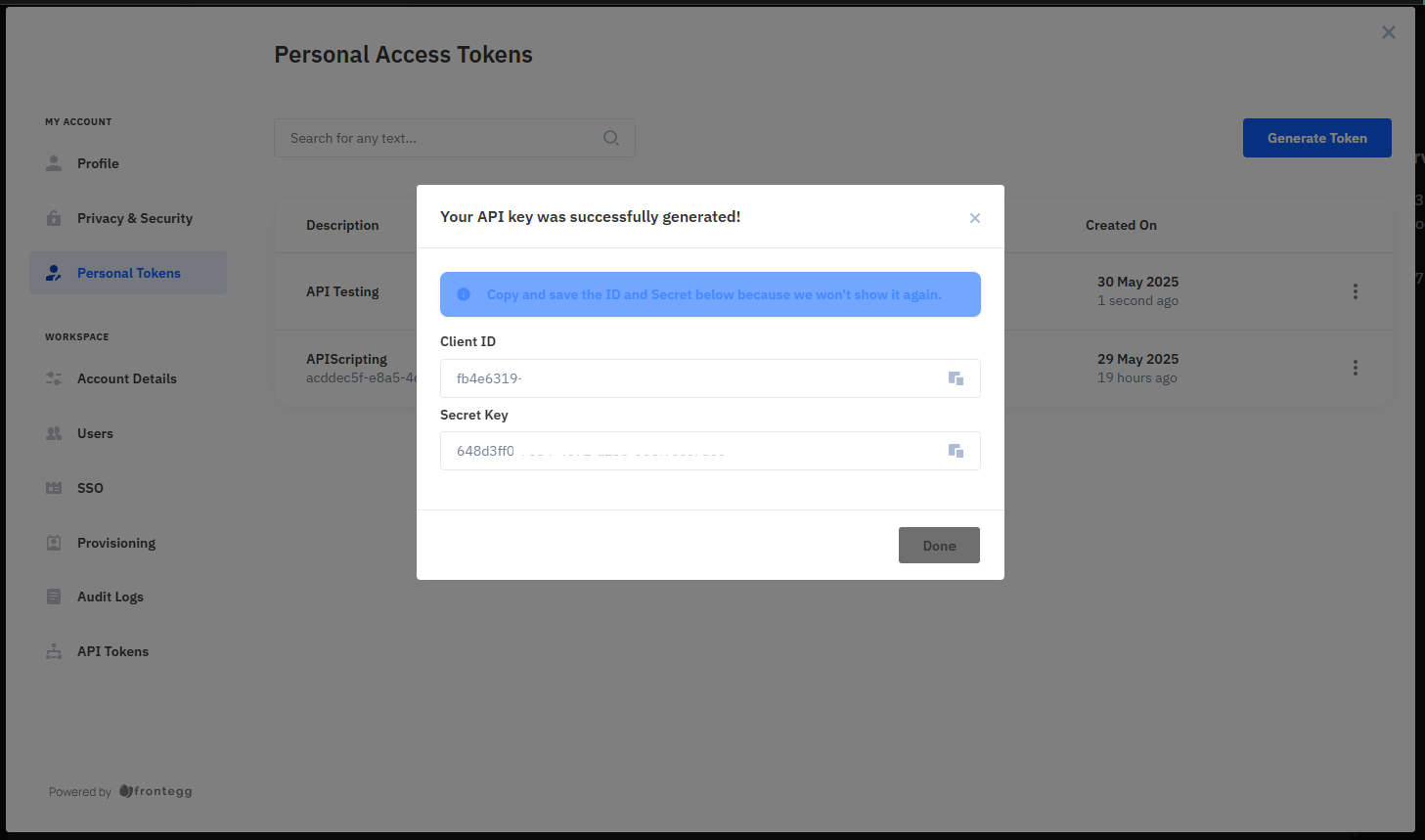
Generate Token:
- Click "Generate Token"
- Provide a description and expiration date
- Click "Create"
-
Save Credentials:
- Record your Client ID and Secret Key in a safe place
- You'll use these credentials in the examples below
Next Steps
Once you have your API credentials, you can proceed with:
- Authentication - Learn how to authenticate with the Causely GraphQL API
- GraphQL Clients - Set up reusable GraphQL client libraries
- Query Examples - Explore example queries and mutations
API Support
For technical questions about the Causely GraphQL API, contact our support team for assistance with integration challenges.