Service Prioritization
Overview
The Service Prioritization feature allows you to assign priority tiers to services discovered within a given scope.
By default, all services are assigned a Service Level Objective (SLO) and treated as Critical.
However, not all services are equally important—some require immediate attention, while others can be deprioritized or hidden entirely.
This feature helps teams focus on what matters, ensuring that high-priority services drive alerts and incident response
while low-priority or internal services remain visible but do not create unnecessary noise.
displayed_sidebar: manageSidebar
How It Works
Each service in a scope can be categorized into one of three Service Tiers:
| Tier | Description |
|---|---|
| Critical: SLO Enforced | Services essential to your business or user experience. Their SLOs are actively enforced. If their SLO is violated or at risk, related root causes are marked Urgent. |
| Non-Critical: SLO Not Enforced | Services that are non-essential or low-impact. These services do not have an active SLO, and their root causes appear in the Root Causes view but are never marked urgent. |
| Hidden: Internal Noise | Internal or auxiliary services you do not want visible in daily operations. Issues impacting these services appear only under the Hidden tab in the Root Causes view. |
displayed_sidebar: manageSidebar
Default Behavior
- Newly discovered services start as Uncategorized, which defaults to Critical: SLO Enforced.
- All services in this state are monitored with an active SLO until explicitly reassigned to another tier.
displayed_sidebar: manageSidebar
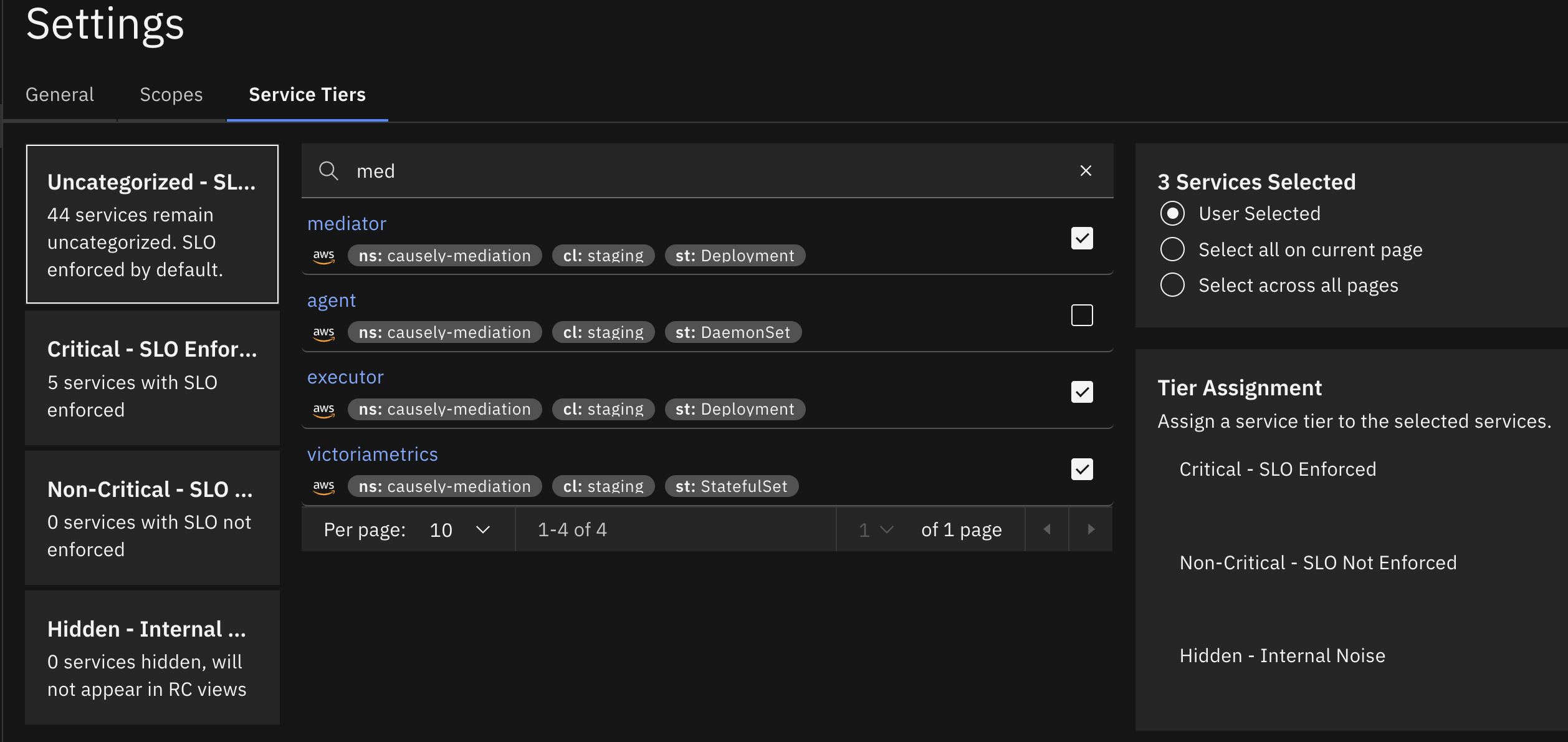
Assigning Service Tiers
- Navigate to Settings → Service Tiers.
- Search or filter for the services you want to prioritize. Note that the available services depend on the currently selected scope.
- Select one or more services.
- Use the Tier Assignment panel to set a tier:
- Critical: SLO Enforced
- Non-Critical: SLO Not Enforced
- Hidden: Internal Noise
You can assign tiers individually or in bulk across pages.
displayed_sidebar: manageSidebar
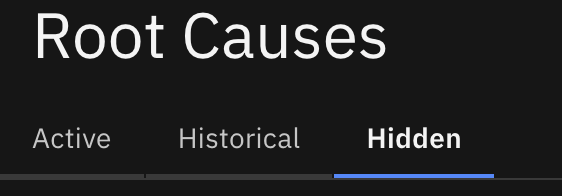
Root Cause Visibility
Tier assignment affects how root causes appear in Root Causes:
- Critical: Appears in Active. Marked Urgent if the SLO is violated or at risk.
- Non-Critical: Appears in Active but never marked urgent.
- Hidden: Appears only in the Hidden tab, not in Active or Historical.
displayed_sidebar: manageSidebar
Example Use Cases
- Critical: Core APIs, payments, authentication, customer-facing services.
- Non-Critical: Internal dashboards, staging workloads, low-traffic utilities.
- Hidden: Background jobs, test services, deprecated components.