v1.0.108
December 23, 2025
Version v1.0.108Expanded Messaging Queue Causal Model
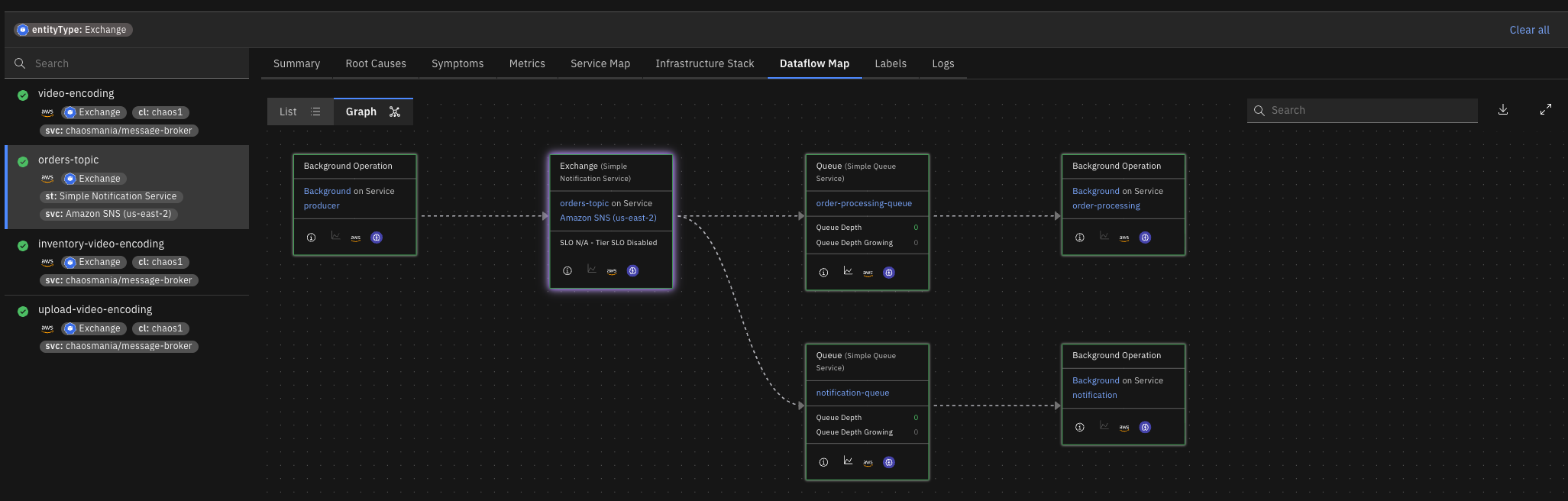
We’ve expanded Causely’s causal model for messaging queues to support richer topologies across common messaging technologies, including Amazon SQS, Amazon SNS, and RabbitMQ. The model now represents exchanges, queues, and data flows in greater detail, enabling more precise causal analysis of messaging-driven systems.
As part of this expansion, we’ve introduced a new root cause focused on unexpected publish rate spikes:
Producer Publish Rate Spike
Service, an HTTP path or RPC method is publishing messages at a significantly higher rate than normal, causing queue depth to grow and producer message rate to increase. This surge creates backpressure and can overwhelm downstream consumers, leading to service degradation.
With this release, Causely now supports both SNS and SQS as first-class messaging technologies.
Expanded Redis Support
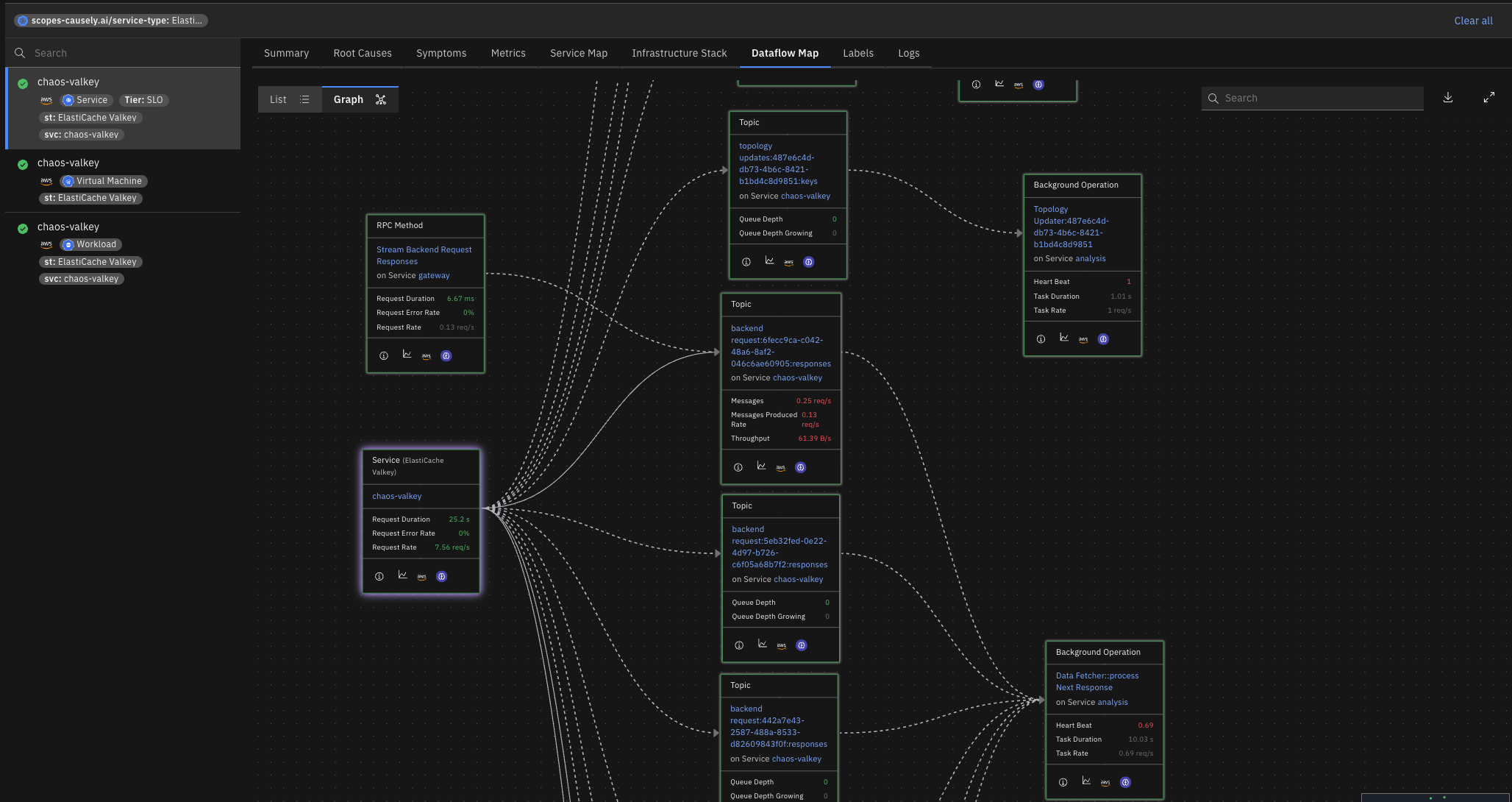
Causely now supports Amazon ElastiCache and Valkey, expanding coverage for managed Redis deployments.
This enables identification of Redis-specific root causes, such as Redis Connection Pool Saturated, while visualizing how data flows to and from managed Redis services across upstream APIs and topics, as well as downstream consumers (see Dataflow Map).
Minor Changes
- Updated root cause display names to clearly emphasize code regressions when issues are caused by recent code changes
- Clarified SLO remaining budget views
- Marked external services with an expected NO-SLO tier
- Filtered external services from service tier views used for service prioritization
- Improved network endpoint normalization to prevent misinterpretation of service-to-service communications caused by inconsistent DNS name resolution