Data Pipeline
Series of processes that move and transform data between systems for analysis, storage, or further processing.
Overview
Database Table
Contention on Database Table Locks
The database table is experiencing an abnormally high rate of exclusive locks, preventing multiple transactions from accessing the table simultaneously. This creates a bottleneck that significantly degrades performance for all client applications depending on this table. Excessive locking typically occurs due to long-running transactions, lock contention between multiple transactions, inefficient transaction design, inappropriate isolation levels, or missing indexes leading to table scans instead of index seeks.
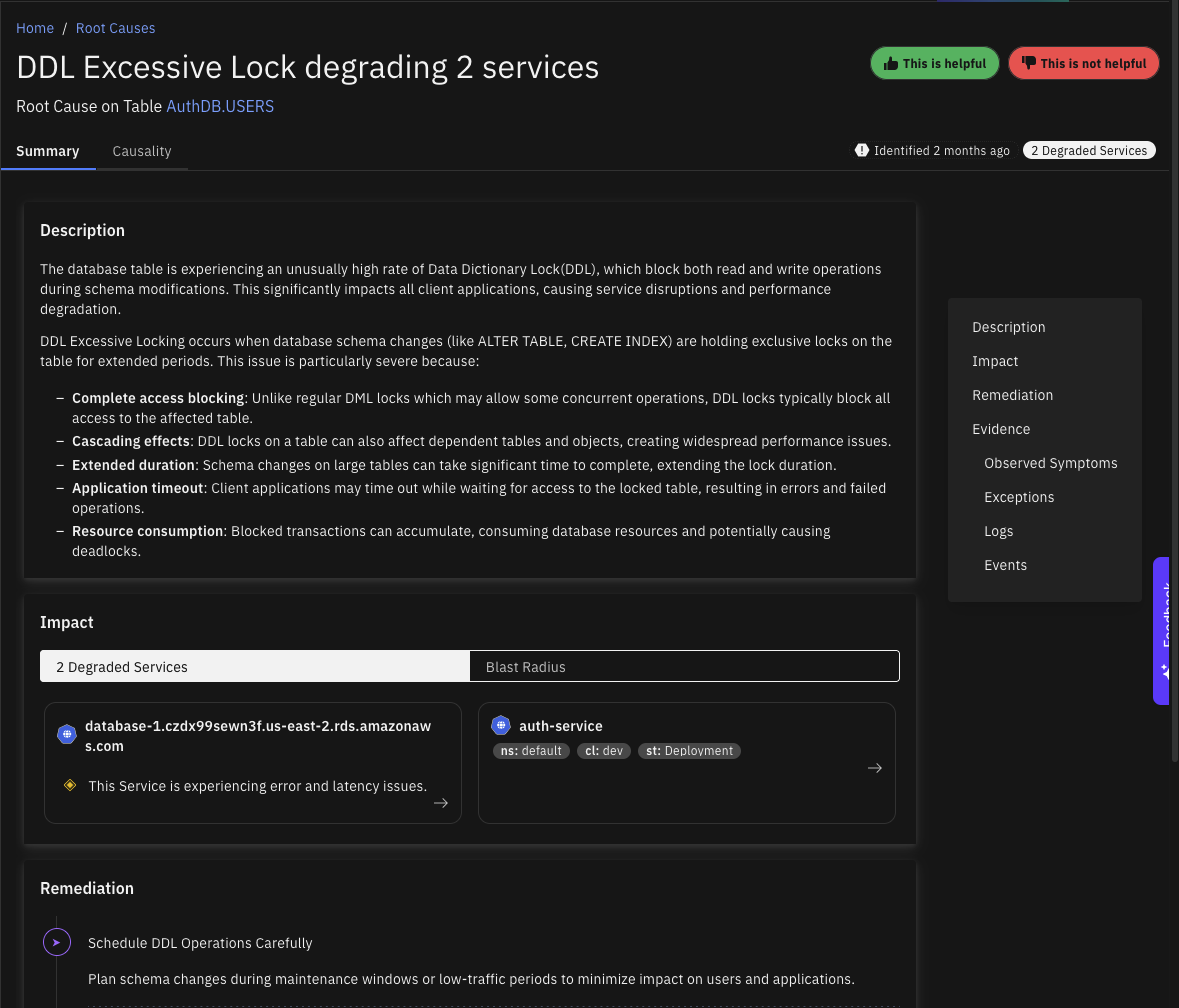
Schema Change Causing Table Lock Contention
The database table is experiencing an unusually high rate of Data Dictionary Lock (DDL), which blocks both read and write operations during schema modifications. This significantly impacts all client applications, causing service disruptions and performance degradation.
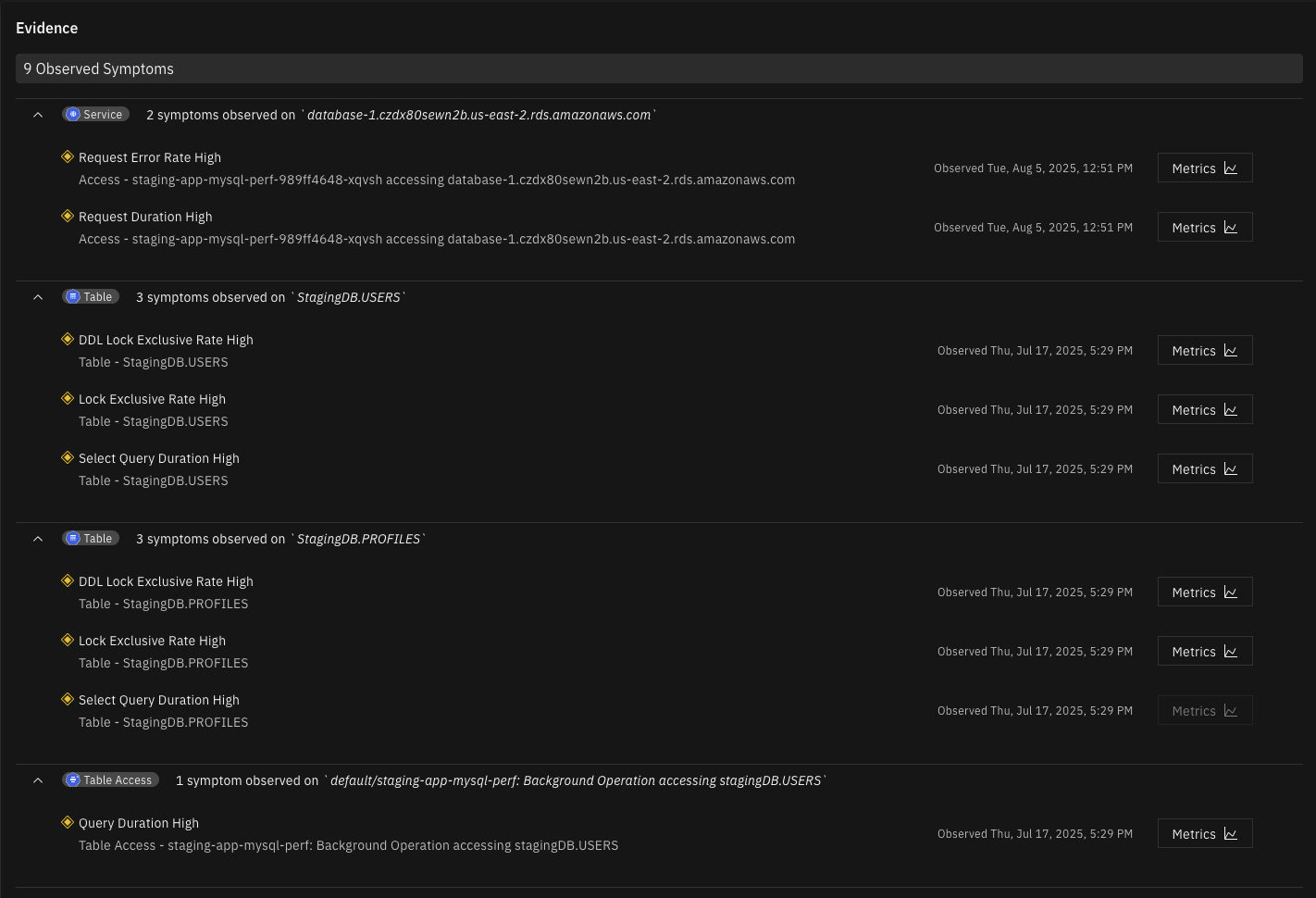
Table Access Failure in Database
The database table is experiencing performance degradation or errors, causing disruptions for client applications. This results in slow query response times, potential errors, and degraded service performance for systems that depend on this table.
HTTP Path
Faulty Error Handling in HTTP Path
The HTTP path is experiencing a high rate of errors, causing disruptions for clients. This can lead to degraded performance, failed requests, or complete service unavailability, significantly affecting the user experience.
Slow Execution in HTTP Path Handler
The HTTP path is experiencing congestion, resulting in high latency for clients. This suggests that the system is unable to handle the current load efficiently, causing delays in response times. Congestion often occurs when the service receives more requests than it can handle within its capacity.
RPC Method
Faulty Error Handling in RPC Method
The RPC Method is experiencing a high rate of errors, causing disruptions for clients. This can lead to degraded performance, failed requests, or complete service unavailability, significantly affecting the user experience.
Slow Execution in RPC Method Handler
The RPC method is experiencing congestion, resulting in high latency for clients. This suggests that the system is unable to handle the current load efficiently, causing delays in response times. Congestion often occurs when the service receives more requests than it can handle within its capacity.